Scientists have shown that a non-invasive sound stimulation of the brain at a specific frequency can clear toxic proteins linked to Alzheimer’s disease, an advance that could lead to low-cost therapy.
Alzheimer’s disease symptoms, including memory loss and problems with language and thinking, are known to be linked to elevated levels of abnormal proteins in the brain called amyloids, which form plaque around cells.
These proteins can build up gradually in the brain and kill the junctions between nerve cells known as synapses, eventually strangling the neurons and causing brain tissue death.
While current treatments improve some symptoms, there are no long-term cures for the debilitating condition.
Now, for the first time, scientists have demonstrated that auditory stimulation at 40Hz can significantly alter amyloid protein levels in the brain of aged rhesus monkeys, with this effect persisting for over five weeks.
The findings suggest 40Hz stimulation could be developed into a non-invasive physical therapy for Alzheimer’s disease (AD) patients.
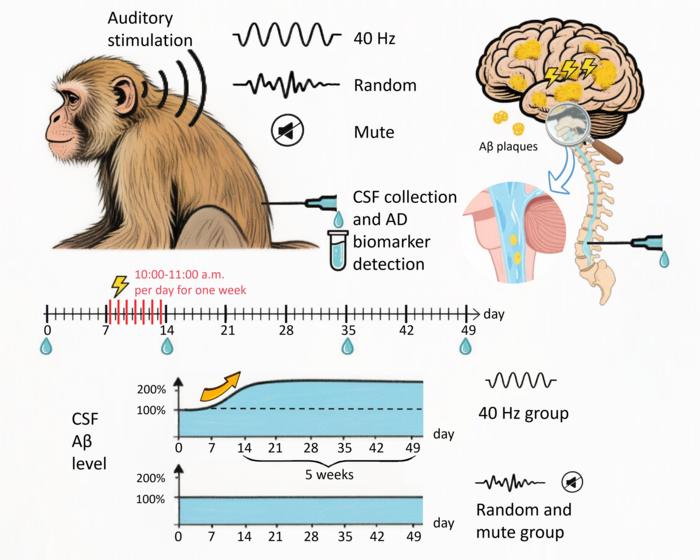
In the study, researchers from the Chinese Academy of Sciences tested the auditory stimulation technique in nine rhesus macaques aged 26–31 years.
The monkeys had developed widespread spontaneous amyloid-β (Aβ) protein clusters in their brains, effectively mimicking the pathological feature of human Alzheimer’s disease, making them an ideal animal research model.
One group of monkeys in the study received an hour of 40Hz auditory stimulation daily for seven consecutive days.
Researchers found that after the sound stimulation, levels of the key amyloid proteins in the monkeys’ spinal fluid (CSF) increased by three times the initial levels.
“Seven days’ stimulation triggered a rapid CSF Aβ increase by more than 200 per cent,” they wrote in the study published in the journal PNAS.
The results are also consistent with previous findings in mouse models, scientists say, suggesting that 40Hz sound stimulation facilitates the clearance of toxic Alzheimer’s-related amyloid proteins from the brain into the spinal fluid.
Scientists found that the amyloid protein levels in the spinal fluid remained elevated when measured five weeks after the stimulation ended, showing there’s a sustained long-term effect from the therapy.
Compared to current antibody treatments to slow early-stage Alzheimer’s disease, researchers say sound stimulation could be developed into a non-invasive, low-cost physical intervention.
“This study provides the first primate evidence that 40Hz auditory stimulation can sustainably modulate the Aβ metabolism in the brain, supporting its potential as a noninvasive AD treatment method,” researchers wrote.


